DHS resets the clock on its threat to stop flyers without ID
Soccer fans have been noticing unusually large amounts of stoppage time added on to extend the final whistle in many of this year’s World Cup matches. But FIFA and World Cup referees have nothing on the US Department of Homeland Security when it comes to extending the end of the game of REAL-ID chicken that the DHS has been playing with air travelers.
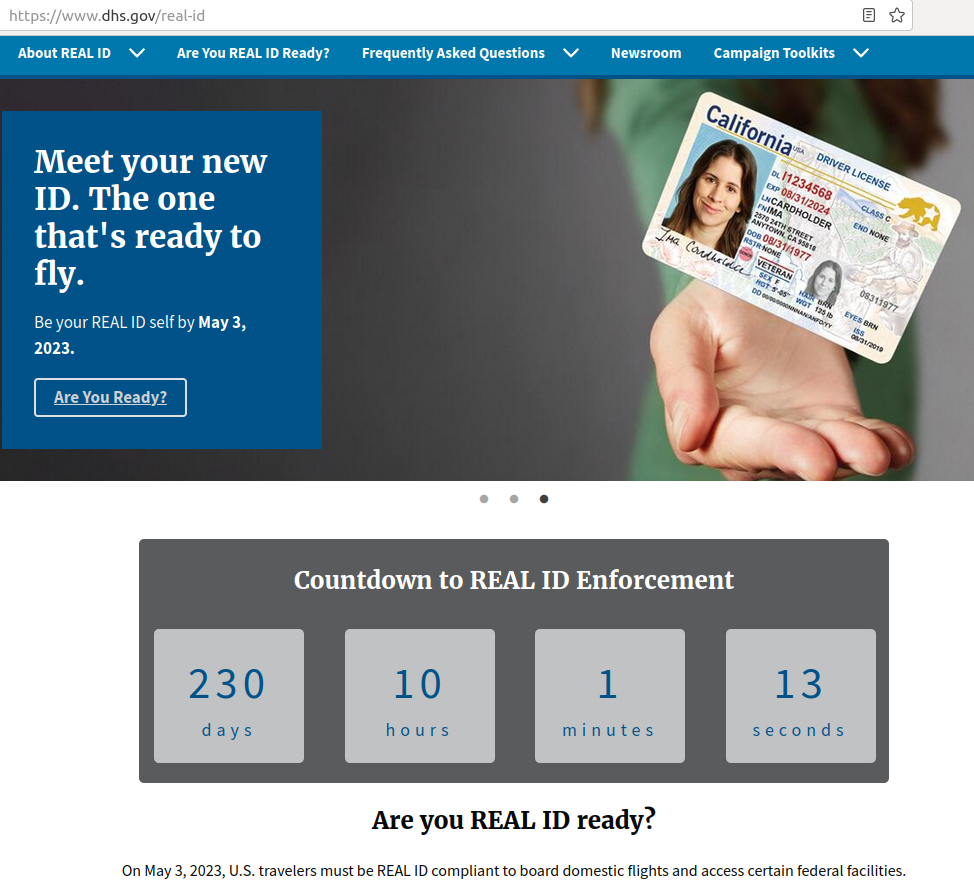
Just a few months after adding a countdown clock to its website to add artistic verisimilitude to its threat to start “enforcing” a nonexistent law prohibiting flying without ID, the DHS has set that clock back by two more years.
The change announced today — only the most recent in a seemingly endless series of postponed empty REAL-ID threats — again postpones, but does not withdraw, the DHS threat to start preventing people without ID from traveling by airline within the US.
The DHS says it plans to promulgate another set of amendments to its regulations implementing the REAL-ID Act of 2005, postponing “enforcement” of the REAL-ID Act at airports until May 7, 2025. Conveniently for current Federal officials, that punts the problem of how to respond to the inevitable resistance to an attempted ban on flying without ID into the next Presidential administration.
Today’s press release from the DHS says, in part:
Under the new regulations, beginning May 7, 2025, every traveler 18 years of age or older will need a REAL ID-compliant driver’s license or identification card, state-issued enhanced driver’s license, or another TSA-acceptable form of identification at airport security checkpoints for domestic air travel.
We doubt, however, that the revised regulations will contain any such provision. None of the previous versions of the REAL-ID regulations contained any provision requiring air travelers to identify themselves, and any such regulatory provision would exceed the implementing authority granted to the DHS by the REAL-ID statute.
The REAL-ID Act restricts what ID credentials a Federal agency can accept, in circumstances where ID is required by some other Federal law or regulation. But neither the REAL-ID Act nor any other current or proposed Federal law or regulation requires travelers to show any ID to pass through Transportation Security Administration checkpoints or board domestic flights within the US — as the TSA itself has argued whenever ID to fly has become an issue in court.
It should go without saying that one doesn’t have to take a “flying test” to obtain a drivers license. A drivers license is not a permit to fly, and possession (or not) of a valid drivers license is entirely unrelated to entitlement to travel by common carrier. The REAL-ID Act has done nothing to make flying safer, any more than preventing people without ID from flying would make flying safer. The only real impact of the REAL-ID Act has been the creation of an (outsourced, privately held, opaque and uncontrolled) national ID database (SPEXS) aggregated from state and territorial driver’s license records.
By the time the two more years of added “stoppage time” runs out on the DHS threat clock, twenty years will have passed since the REAL-ID Act was rushed through Congress in post-9/11 panic, without debate and with hardly time for legislators to read the bill.
Time is running out on the REAL-ID Act. It’s time for Congress to admit that the REAL-ID Act was wrong from the start, has enabled the creation of a de facto national ID database overwhelmingly opposed by the American public, and should be repealed.