100,000 passport applicants have gotten the long form
More than 100,000 US citizens — almost ten times as many as the State Department had projected — have been required to complete one or both of two impossible “long form” supplements to their applications for US passports, according to records we received this month in response to a Freedom Of Information Act (FOIA) request we filed in 2011.
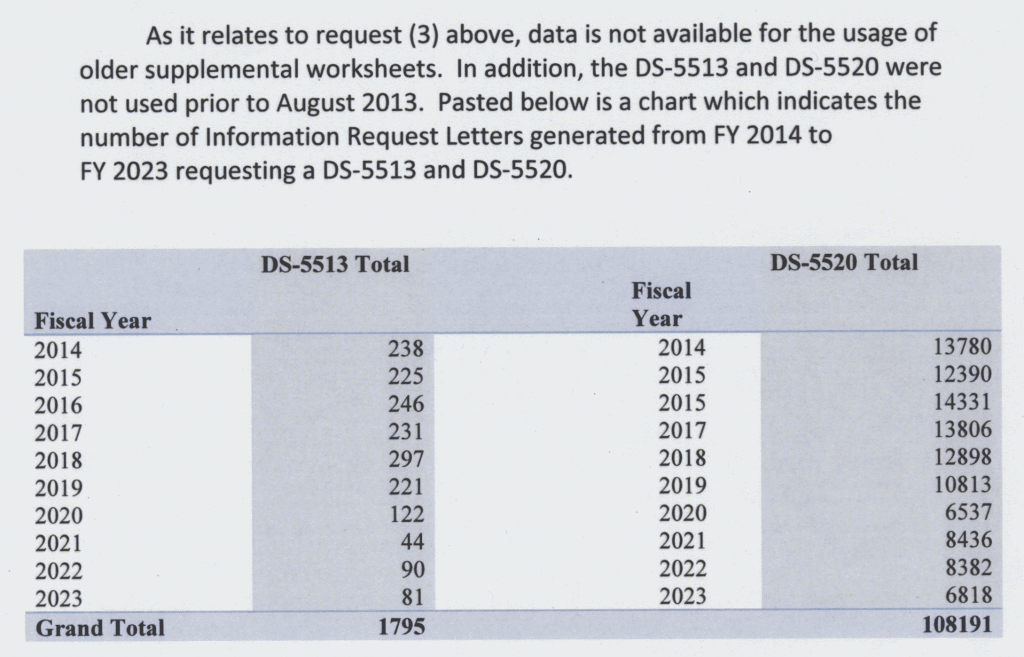 [Numbers of passport applicants sent each of the two version of the long form passport application each year since 2014, as reported to us this month by the State Department in response to our 2011 FOIA request.]
[Numbers of passport applicants sent each of the two version of the long form passport application each year since 2014, as reported to us this month by the State Department in response to our 2011 FOIA request.]
Back in 2011, the State Department proposed an outrageous long form to be sent to some subset of applicants for US passports. The form includes a bizarre list of questions which most applicants would be unable to answer.
Do you know, or do you have any way to find out, the dates, addresses, and names of doctors for each of your mother’s pre-natal medical appointments, or the names, addresses, and phone numbers of everyone who was in the room when you were born?
Sending someone the supplemental long form is a pretext for denying their application for a passport. As we said in our comments to the State Department:
The proposed form reminds us unpleasantly of the invidious historic “Jim Crow” use of a literacy or civics test of arbitrary difficulty, required as a condition of registering to vote and administered in a standardless manner. By making the test impossible to pass, voter registrars could use it as an arbitrary and discriminatory – but facially neutral – excuse to prevent any applicant to whom they chose to give a sufficiently difficult test from registering to vote, on the ostensible basis of their having “failed” the test.
In a similar way, choosing to require an applicant for a passport to complete the proposed Form DS-5513, which few if any applicants could complete, would amount to a de facto decision to deny that applicant a passport. And that decision would be standardless, arbitrary, and illegal.
After we publicized this proposal, thousands of people submitted comments to the State Department calling for the proposed form to be withdrawn.
Although the State Department had falsely claimed in its application for approval that this was a “new” form, commenters reported that they had already (illegally) been required to fill out a version of this form, even though it had not been approved.
As soon as we learned this, we filed a Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) request in April 2011 to find out how long the long form had been in use illegally without approval, how many people had been told to fill out the long form, and what if any criteria had been established for when to require a passport applicant to fill out the long form.

