A new report by the DHS Office of Inspector General (OIG) gives perhaps the most detailed official picture to date of the US government’s plans for ed biometric identification, tracking, and control of international air travelers through automated facial recognition.
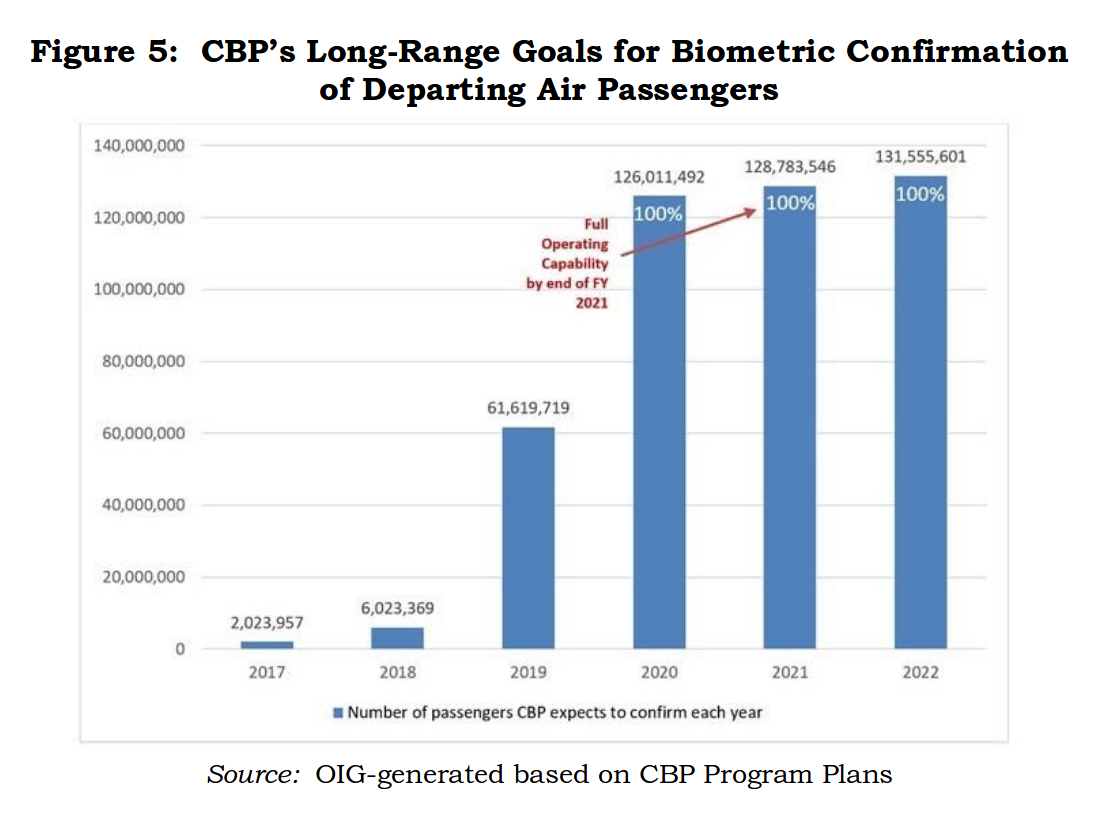
Contrary to specious claims in DHS propaganda that the current rollout of mug-shot machines at departure gates at airports across the country is “only a test,” the DHS OIG reports that US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) plans to expand the mug shot and automated facial image recognition program from 6 million air travelers in 2018 to 60 million in 2019, 120 million in 2020, and 129 million — 100% of international airline departures from the US — by 2021.
But that’s not all. “Over time, the program plans to … incrementally deploy biometric capabilities across all modes of travel — air, sea, and land — by fiscal year 2025,” according to the OIG report.
The scope of these plans should make clear that the only thing being “tested” is whether travelers will submit to this program, not whether it is justified or what interests it serves.
The OIG report mentions that US citizens have been “allowed” to opt out of the airport mug shot “pilot program “, but doesn’t say whether they were told they had a right to do so:
CBP allowed U.S. citizens to decline participation in the pilot. In such cases, CBP officers would permit the travelers to bypass the camera and would instead check the individuals’ passports to verify U.S. citizenship. When a U.S. citizen opted to participate in the pilot but did not successfully match with a gallery photo, the CBP officer would examine the individual’s passport but did not collect fingerprints. We observed biometric screening at four airports — a total of 12 flights — during our audit and witnessed only 16 passengers who declined to participate.
 [Note the absence of any apparent notice that US citizens can “opt-out”.]
[Note the absence of any apparent notice that US citizens can “opt-out”.]
In preparing their report, OIG staff “met with a number of external stakeholders, including the Airlines for America trade association, Delta Airlines, JetBlue Airlines, and British Airways.” Notably, however, OIG made no attempt to consult consumer, civil liberties, or human rights organizations or to consider their objections to mandatory mug shots.
The only objections noted in the OIG report came from airlines and airport operators. But it would be a mistake to interpret this as “resistance” from the airline industry to biometric surveillance of airline passengers through automated facial recognition.
The OIG report makes clear that the only thing being disputed by airlines and airports is who will pay for equipment and staff, not whether these systems will be deployed: Read More →