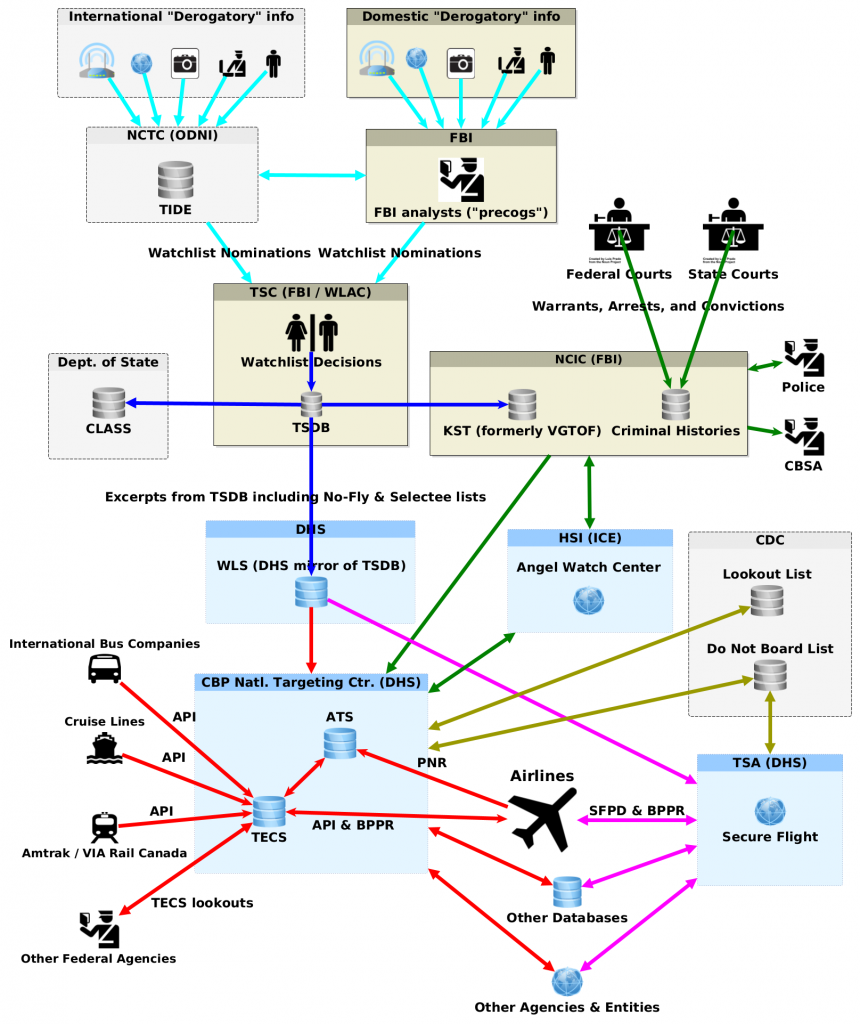
ID demand was unconstitutional, but sheriffs get “qualified immunity”
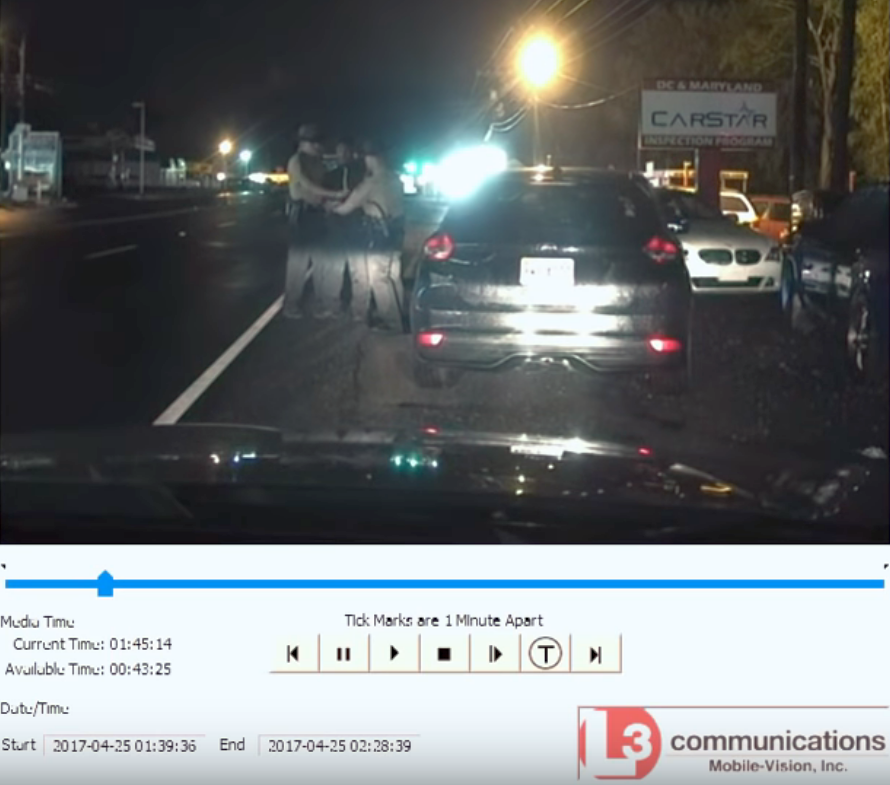 [Dashcam video of George Wingate being wrongfully arrested by Stafford County, VA Deputy Sheriffs, April 2017]
[Dashcam video of George Wingate being wrongfully arrested by Stafford County, VA Deputy Sheriffs, April 2017]
In its 2004 decision in Hiibel v. Nevada, 2004, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld a demand for a pedestrian to identify himself to police only on the basis that (1) there was already a reasonable articulable basis for suspicion that he had committed some crime before the police demanded that he identify himself, and (2) the state law at issue, as interpreted by the Supreme Court, required only verbal self-identification (“My name is John Smith”) and not the production of ID credentials or other evidence of his identity.
You might think that a precedent established by the Supreme Court would be “clearly established”. But that would often be wrong, at least in the topsy-turvy world “qualified immunity“.
Some Federal Court of Appeals have held that police who unconstitutionally demand ID can be held liable for violating the civil rights of their victims — as, of course, they should be.
In other cases, however, such as that of Philip Mocek, Courts of Appeal have let ID-demanding police off the hook. The judges theory in these cases has been that, although the police demands for ID were unconstitutional, that illegality wasn’t yet “clearly established. The police might, judges speculated, have had a good-faith, although mistaken, belief that they had a right to demand ID in the particular circumstances at issue.
The latest example of this strained excuse for police impunity comes from the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals in its recent decision in Wingate v. Fulford.
George Wingate was accosted by Stafford County, VA, Deputy Sheriffs while standing by his car, which he had pulled off the road to try to diagnose the cause of an engine warning light. Nothing about the circumstances gave the sheriffs reason to suspect Mr. Wingate of any crime, the court found. But the sheriffs nonetheless wanted to know who he was.
As captured on this dashcam video, Mr. Wingate knew and properly asserted his rights. The conversation between Mr. Wingate and Deputy Sheriff Scott Fulford went like this:
Fulford: Well, in Stafford County —
Wingate: Have I committed a crime?
Fulford: — it’s required.
Wingate: Have I committed a crime?
Fulford: No. I didn’t say you did.
Wingate: All right then.
Fulford: You’re still required to —
Wingate: Am I free to go?
Fulford: — identify yourself.
Wingate: Am I free to go?
Fulford: Not right now, no.
Wingate: Am I being detained?
Fulford: You’re not detained.
Wingate: Am I free to go?
Fulford: No.
Wingate: Am I being detained? If I’m not being detained, then I’m free to go.
Fulford: You’re not free to go until you identify yourself to me.
All this was, the Court of Appeals found, unconstitutional. And “You’re not being detained, but you’re not free to go” sound a lot more like a pretext for logging the identity and movements of a Black man than good faith. But the Court of Appeals let Fulford and his partner, Deputy Sheriff Dimas Pinzon, off scott-free for their false arrest of Mr. Wingate on the basis of qualified immunity (although they did allow Mr. Wingate to proceed with his case against the police for falsely detaining him in the first place).
Congress needs to end this nonsense by repealing qualified immunity.