The DHS FOIA Office “is not in service”
We’ve been waiting for years for responses to some of our FOIA requests to the TSA and DHS, including a request for records of what happened to our earlier FOIA requests that were subjected to a special program of political review and reporting to the White House, a request for records that were previously improperly withheld under a claimed FOIA “exemption” which the Supreme Court eventually ruled didn’t exist, and a request for any records of the TSA having sought or obtained OMB approval for its Certification of Identity form.
Unfortunately, the de facto policy of the Department of Homeland Security is not just to ignore any FOIA requester who isn’t already suing it, but to make it impossible even to communicate with it or obtain proof of having made requests.
As we’ve noted before, the DHS uses a contractor who often fails either to deliver their mail or return the return receipts, making it impossible to prove they have received requests. Recipients have told us that the mail is often so browned and burnt by the contractor’s high-intensity x-ray screening that mail that is eventually delivered to DHS, after a delay of a week or so, is often illegible.
Despite huge expansion, changes, reorganizations, and relocations of DHS offices, the DHS FOIA Regulations and what is required by law to be the definitive list of DHS FOIA contacts hasn’t been updated since 2003, despite our repeated protests. Today, many of those addresses lead only to the dead-letter office.
Many DHS and component offices don’t disclose their physical locations. Even if you can find where their offices are, the doors are barred to those without appointments and government-issued photo ID.
And it’s getting worse. Now the main phone number for the DHS FOIA Requester Service Center (and, if you want to complain about their unresponsiveness, the DHS FOIA “Public Liaison” as well), has been disconnected or taken out of service. Not that it was usually answered by a human being, or that voicemail messages were usually returned, but turning off the phones entirely (or using only some other undisclosed phone numbers at their undisclosed location) is really a new low.
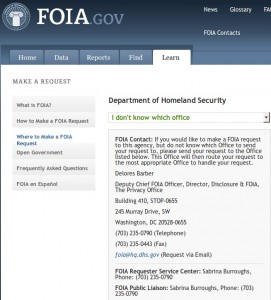
If you go to the Where to Make a FOIA Request page on FOIA.gov, and choose “Department of Homeland Security” and then either “Headquarters and Privacy Office” or “I don’t know which office”, you are directed to call (703) 235-0790. (Click the image above for a larger version of the Web page.) Call that number, and you get the recorded message, “Sorry. The number you have reached is not in service.”
We knew the DHS FOIA Office was “not in service”, or at least not serving us. But we didn’t realize that they had gotten the phone company to put a recording on their line telling that to anyone who tries to call.
[Update: The TSA and DHS claim that the “FOIA.gov” website is maintained by the Department of Justice and beyond the control of the DHS. But the same wrong number appears on DHS.gov at http://www.dhs.gov/check-status-your-foia-request as the number to call to find out the status of a FOIA request, along with a self-referential hyperlink for FOIA status information that links back to the same page.]